Wireless Sniffing with Kali Linux
Software
- Virtual machine (VMWare, VirtualBox, KVM, ...)
- Kali Linux 2017.2 in virtual machine
Hardware
- Panda Wireless N600 Dual Band Wireless-N USB Adapter
- 802.11 b/g/n 2.4GHz
- 802.11 ac/n 5GHz
- Uses Ralink RT5572 chipset
- MIMO 2x2 only
- Lab Network (configured to ensure USB adapter can capture all traffic)
- SSID:
cyberlab-ctc214-Student-2.4GHz- Channel: 11 (2462 MHz, 20MHz channel, No extension channel)
- 802.11g/n
- MIMO 2x2 (not 3x3 as AP is capable of) - HT MCS 0-15
- SSID:
cyberlab-ctc214-Student- Channel 165 (5825 MHz, 20MHz channel, No extension channel)
- 802.11 n/ac
- MIMO 2x2 (not 3x3 as AP is capable of) - HT MCS 0-15
- No VHT (disabled)
- SSID:
Network Capture
Download Kali Linux ISO from https://www.kali.org/ and install into a virtual machine
Connect the USB WiFi Adapter. In your virtual machine, attach that USB device (labeled Ralink 802.11 n WLAN) directly to your Kali Linux VM.
Install VM tools in Kali to improve integration:
$ sudo apt-get install open-vm-tools open-vm-tools-desktopVerify that the USB adapter is visible in Kali:
$ lsusb
# Should see Ralink Technology, Corp. RT5572 Wireless AdapterVerify that the network interface is visible in Kali:
$ ifconfig
# Should see network interface with one of two names:
# 'wlanN' where N is an integer
# 'wlxXXXXXXXXXXXX' where XX... is MAC address of interfaceConfigure Network Manager to stop managing the wireless device
$ gedit /etc/NetworkManager/NetworkManager.conf &
#
# Add these two lines at the bottom of the .conf file:
[keyfile]
unmanaged-devices=interface-name:wlan0;interface-name:wlan1;interface-name:wlan2;interface-name:wlan3Put the network interface in monitor mode and specify the channel used by cyberlab-XXX wireless network:
$ ifconfig wlan0 down
$ iwconfig wlan0 mode monitor channel XXXX
# where XXX is channel, i.e. 11 or 165 in standard lab configuration
$ ifconfig wlan0 upLaunch Wireshark.
- Under Edit->Preferences->Protocols->IEEE 802.11, ensure that "Enable Decryption" is checked
- Under Edit->Preferences->Protocols->IEEE 802.11->Decryption Keys, enter the password for the cyberlab-XXX network you are passively monitoring and wish to decrypt.
- Choose key type "wpa-pwd"
- For the key, use the format
password:SSIDto explicitly tell Wireshark what SSID the password corresponds to. For passwords or SSIDs that contain spaces, use URI-style percent escapes, e.g. %20 for a space. - For additional configuration tips, see: https://wiki.wireshark.org/HowToDecrypt802.11
- Begin capturing data on the 'wlan0' interface.
When finished with data capture, restore the network interface:
ifconfig wlan0 down
iwconfig wlan0 mode managed channel auto
ifconfig wlan0 upVerification
Wireshark has a very long list of 802.11 display filters you can choose from. Some of the more useful filters are:
wlan- Show only 802.11 frameswlan.addr==08.00.08.15.ca.fe- Show only 802.11 frames to or from a specific MAC addresswlan.ssid=="cyberlab-ctc214-Student- Show only 802.11 management frames for the SSID cyberlab-ctc214-studenteapol- Show only 802.1x EAPOL authentication messages
Other filters let you dig into the specific frame types:
| Frame Type | Wireshark Filter |
|---|---|
| Management frames | wlan.fc.type==0 |
| Control frames (RTS, CTS, ACKs, ...) | wlan.fc.type==1 |
| Data frames | wlan.fc.type==2 |
| Frame Subtype | Wireshark Filter |
|---|---|
| Association request | wlan.fc.type_subtype==0 |
| Association response | wlan.fc.type_subtype==1 |
| Probe request | wlan.fc.type_subtype==4 |
| Probe response | wlan.fc.type_subtype==5 |
| Beacon | wlan.fc.type_subtype==8 |
| Disassociate | wlan.fc.type_subtype==10 |
| Authentication | wlan.fc.type_subtype==11 |
| Deauthentication | wlan.fc.type_subtype==12 |
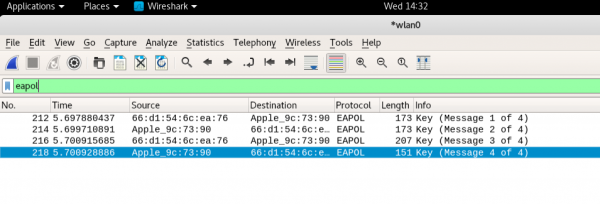
For Wireshark to decrypt client traffic using the key you entered, it must capture the initial 4-way handshake. You can check if you captured the 4-way handshake by using a Wireshark filter of eapol. You should see 'Message n of 4' printed 4 times for each client.
Debugging Information
There are a variety of commands in Linux to learn more about your wireless network interface and nearby access points.
Show list of wireless devices (e.g. phy0) and the wireless interfaces (e.g. wlan0) associated with it:
$ iw dev
phy#0
Interface wlan0
ifindex 3
wdev 0x1
addr 9c:ef:d5:fe:bb:ce
type managed
txpower 0.00 dBmShow capabilities of the wireless PHY hardware:
$ iw phy phy0 info
Wiphy phy0
max # scan SSIDs: 4
max scan IEs length: 2257 bytes
max # sched scan SSIDs: 0
max # match sets: 0
max # scan plans: 1
max scan plan interval: -1
max scan plan iterations: 0
Retry short long limit: 2
Coverage class: 0 (up to 0m)
Device supports RSN-IBSS.
Supported Ciphers:
* WEP40 (00-0f-ac:1)
* WEP104 (00-0f-ac:5)
* TKIP (00-0f-ac:2)
* CCMP-128 (00-0f-ac:4)
* CCMP-256 (00-0f-ac:10)
* GCMP-128 (00-0f-ac:8)
* GCMP-256 (00-0f-ac:9)
Available Antennas: TX 0 RX 0
Supported interface modes:
* IBSS
* managed
* AP
* AP/VLAN
* monitor
* mesh point
Band 1:
Capabilities: 0x2fe
HT20/HT40
SM Power Save disabled
RX Greenfield
RX HT20 SGI
RX HT40 SGI
TX STBC
RX STBC 2-streams
Max AMSDU length: 3839 bytes
No DSSS/CCK HT40
Maximum RX AMPDU length 65535 bytes (exponent: 0x003)
Minimum RX AMPDU time spacing: 2 usec (0x04)
HT TX/RX MCS rate indexes supported: 0-15, 32
Bitrates (non-HT):
* 1.0 Mbps
* 2.0 Mbps (short preamble supported)
* 5.5 Mbps (short preamble supported)
* 11.0 Mbps (short preamble supported)
* 6.0 Mbps
* 9.0 Mbps
* 12.0 Mbps
* 18.0 Mbps
* 24.0 Mbps
* 36.0 Mbps
* 48.0 Mbps
* 54.0 Mbps
Frequencies:
* 2412 MHz [1] (20.0 dBm)
* 2417 MHz [2] (20.0 dBm)
* 2422 MHz [3] (20.0 dBm)
* 2427 MHz [4] (20.0 dBm)
* 2432 MHz [5] (20.0 dBm)
* 2437 MHz [6] (20.0 dBm)
* 2442 MHz [7] (20.0 dBm)
* 2447 MHz [8] (20.0 dBm)
* 2452 MHz [9] (20.0 dBm)
* 2457 MHz [10] (20.0 dBm)
* 2462 MHz [11] (20.0 dBm)
* 2467 MHz [12] (20.0 dBm) (no IR)
* 2472 MHz [13] (20.0 dBm) (no IR)
* 2484 MHz [14] (20.0 dBm) (no IR)
Band 2:
Capabilities: 0x2fe
HT20/HT40
SM Power Save disabled
RX Greenfield
RX HT20 SGI
RX HT40 SGI
TX STBC
RX STBC 2-streams
Max AMSDU length: 3839 bytes
No DSSS/CCK HT40
Maximum RX AMPDU length 65535 bytes (exponent: 0x003)
Minimum RX AMPDU time spacing: 2 usec (0x04)
HT TX/RX MCS rate indexes supported: 0-15, 32
Bitrates (non-HT):
* 6.0 Mbps
* 9.0 Mbps
* 12.0 Mbps
* 18.0 Mbps
* 24.0 Mbps
* 36.0 Mbps
* 48.0 Mbps
* 54.0 Mbps
Frequencies:
* 5180 MHz [36] (20.0 dBm) (no IR)
* 5190 MHz [38] (20.0 dBm) (no IR)
* 5200 MHz [40] (20.0 dBm) (no IR)
* 5210 MHz [42] (20.0 dBm) (no IR)
* 5220 MHz [44] (20.0 dBm) (no IR)
* 5230 MHz [46] (20.0 dBm) (no IR)
* 5240 MHz [48] (20.0 dBm) (no IR)
* 5250 MHz [50] (disabled)
* 5260 MHz [52] (20.0 dBm) (no IR, radar detection)
* 5270 MHz [54] (20.0 dBm) (no IR, radar detection)
* 5280 MHz [56] (20.0 dBm) (no IR, radar detection)
* 5290 MHz [58] (20.0 dBm) (no IR, radar detection)
* 5300 MHz [60] (20.0 dBm) (no IR, radar detection)
* 5310 MHz [62] (20.0 dBm) (no IR, radar detection)
* 5320 MHz [64] (20.0 dBm) (no IR, radar detection)
* 5500 MHz [100] (20.0 dBm) (no IR, radar detection)
* 5510 MHz [102] (20.0 dBm) (no IR, radar detection)
* 5520 MHz [104] (20.0 dBm) (no IR, radar detection)
* 5530 MHz [106] (20.0 dBm) (no IR, radar detection)
* 5540 MHz [108] (20.0 dBm) (no IR, radar detection)
* 5550 MHz [110] (20.0 dBm) (no IR, radar detection)
* 5560 MHz [112] (20.0 dBm) (no IR, radar detection)
* 5570 MHz [114] (20.0 dBm) (no IR, radar detection)
* 5580 MHz [116] (20.0 dBm) (no IR, radar detection)
* 5590 MHz [118] (20.0 dBm) (no IR, radar detection)
* 5600 MHz [120] (20.0 dBm) (no IR, radar detection)
* 5610 MHz [122] (20.0 dBm) (no IR, radar detection)
* 5620 MHz [124] (20.0 dBm) (no IR, radar detection)
* 5630 MHz [126] (20.0 dBm) (no IR, radar detection)
* 5640 MHz [128] (20.0 dBm) (no IR, radar detection)
* 5650 MHz [130] (20.0 dBm) (no IR, radar detection)
* 5660 MHz [132] (20.0 dBm) (no IR, radar detection)
* 5670 MHz [134] (20.0 dBm) (no IR, radar detection)
* 5680 MHz [136] (20.0 dBm) (no IR, radar detection)
* 5690 MHz [138] (20.0 dBm) (no IR, radar detection)
* 5700 MHz [140] (20.0 dBm) (no IR, radar detection)
* 5745 MHz [149] (20.0 dBm) (no IR)
* 5755 MHz [151] (20.0 dBm) (no IR)
* 5765 MHz [153] (20.0 dBm) (no IR)
* 5775 MHz [155] (20.0 dBm) (no IR)
* 5785 MHz [157] (20.0 dBm) (no IR)
* 5795 MHz [159] (20.0 dBm) (no IR)
* 5805 MHz [161] (20.0 dBm) (no IR)
* 5825 MHz [165] (20.0 dBm) (no IR)
* 4920 MHz [184] (disabled)
* 4940 MHz [188] (disabled)
* 4960 MHz [192] (disabled)
* 4980 MHz [196] (disabled)
Supported commands:
* new_interface
* set_interface
* new_key
* start_ap
* new_station
* new_mpath
* set_mesh_config
* set_bss
* authenticate
* associate
* deauthenticate
* disassociate
* join_ibss
* join_mesh
* set_tx_bitrate_mask
* frame
* frame_wait_cancel
* set_wiphy_netns
* set_channel
* set_wds_peer
* probe_client
* set_noack_map
* register_beacons
* start_p2p_device
* set_mcast_rate
* connect
* disconnect
* set_qos_map
* Unknown command (121)
Supported TX frame types:
* IBSS: 0x00 0x10 0x20 0x30 0x40 0x50 0x60 0x70 0x80 0x90 0xa0 0xb0 0xc0 0xd0 0xe0 0xf0
* managed: 0x00 0x10 0x20 0x30 0x40 0x50 0x60 0x70 0x80 0x90 0xa0 0xb0 0xc0 0xd0 0xe0 0xf0
* AP: 0x00 0x10 0x20 0x30 0x40 0x50 0x60 0x70 0x80 0x90 0xa0 0xb0 0xc0 0xd0 0xe0 0xf0
* AP/VLAN: 0x00 0x10 0x20 0x30 0x40 0x50 0x60 0x70 0x80 0x90 0xa0 0xb0 0xc0 0xd0 0xe0 0xf0
* mesh point: 0x00 0x10 0x20 0x30 0x40 0x50 0x60 0x70 0x80 0x90 0xa0 0xb0 0xc0 0xd0 0xe0 0xf0
* P2P-client: 0x00 0x10 0x20 0x30 0x40 0x50 0x60 0x70 0x80 0x90 0xa0 0xb0 0xc0 0xd0 0xe0 0xf0
* P2P-GO: 0x00 0x10 0x20 0x30 0x40 0x50 0x60 0x70 0x80 0x90 0xa0 0xb0 0xc0 0xd0 0xe0 0xf0
* P2P-device: 0x00 0x10 0x20 0x30 0x40 0x50 0x60 0x70 0x80 0x90 0xa0 0xb0 0xc0 0xd0 0xe0 0xf0
Supported RX frame types:
* IBSS: 0x40 0xb0 0xc0 0xd0
* managed: 0x40 0xd0
* AP: 0x00 0x20 0x40 0xa0 0xb0 0xc0 0xd0
* AP/VLAN: 0x00 0x20 0x40 0xa0 0xb0 0xc0 0xd0
* mesh point: 0xb0 0xc0 0xd0
* P2P-client: 0x40 0xd0
* P2P-GO: 0x00 0x20 0x40 0xa0 0xb0 0xc0 0xd0
* P2P-device: 0x40 0xd0
software interface modes (can always be added):
* AP/VLAN
* monitor
valid interface combinations:
* #{ AP, mesh point } <= 8,
total <= 8, #channels <= 1
HT Capability overrides:
* MCS: ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff
* maximum A-MSDU length
* supported channel width
* short GI for 40 MHz
* max A-MPDU length exponent
* min MPDU start spacing
Device supports TX status socket option.
Device supports HT-IBSS.
Device supports SAE with AUTHENTICATE command
Device supports low priority scan.
Device supports scan flush.
Device supports AP scan.
Device supports per-vif TX power setting
Driver supports full state transitions for AP/GO clients
Driver supports a userspace MPM
Device supports configuring vdev MAC-addr on create.Show information about the AP you are associated with (if any):
$ iwconfig wlan0
wlan0 IEEE 802.11abgn ESSID:"Pacific_Guest"
Mode:Managed Frequency:5.22 GHz Access Point: 00:3A:7D:04:32:AE
Bit Rate=54 Mb/s Tx-Power=15 dBm
Retry short limit:7 RTS thr:off Fragment thr:off
Power Management:on
Link Quality=70/70 Signal level=-38 dBm
Rx invalid nwid:0 Rx invalid crypt:0 Rx invalid frag:0
Tx excessive retries:0 Invalid misc:0 Missed beacon:0Show information about the AP you are associated with (if any):
$ iw dev wlan0 link
Connected to 00:3a:7d:0b:42:de (on wlx9cefd5febbce)
SSID: Pacific_Guest
freq: 5765
RX: 245231 bytes (3322 packets)
TX: 7119 bytes (74 packets)
signal: -52 dBm
tx bitrate: 18.0 MBit/s
bss flags: short-slot-time
dtim period: 1
beacon int: 102$ iw dev wlan0 station dump
Station 00:3a:7d:0b:42:de (on wlx9cefd5febbce)
inactive time: 868 ms
rx bytes: 272547
rx packets: 3693
tx bytes: 7422
tx packets: 78
tx retries: 32
tx failed: 3
signal: -56 dBm
signal avg: -54 dBm
tx bitrate: 18.0 MBit/s
rx bitrate: 54.0 MBit/s
expected throughput: 12.359Mbps
authorized: yes
authenticated: yes
preamble: long
WMM/WME: no
MFP: no
TDLS peer: noShow LENGTHY details about all access points within range and their capabilities:
$ sudo iw dev wlan0 scan
... Will show LENGTHY detailsAlternate Method (airmon-ng)
Alternate method, using airmon-ng tools:
# Check for wireless interface:
$ airmon-ng
# Should see:
# PHY Interface Driver Chipset
# phy0 wlan0 rt2800usb Ralink Technology, Corp. RT5572
# Check for processes that might interfere with monitor mode:
$ airmon-ng check
# Should see:
# Found 2 processes that could cause trouble.
# If airodump-ng, aireplay-ng or airtun-ng stops working after
# a short period of time, you may want to run 'airmon-ng check kill'
#
# PID Name
# 552 NetworkManager
# 1332 wpa_supplicant
# Kill processes that might prevent USB WiFi from entering monitor mode:
$ airmon-ng kill
# Set USB WiFi to monitor mode
$ airmong-ng start wlan0 165
# Begin wireshark capture on new interface that was created: wlan0mon
# Cleanup
$ airmon-ng stop wlan0mon